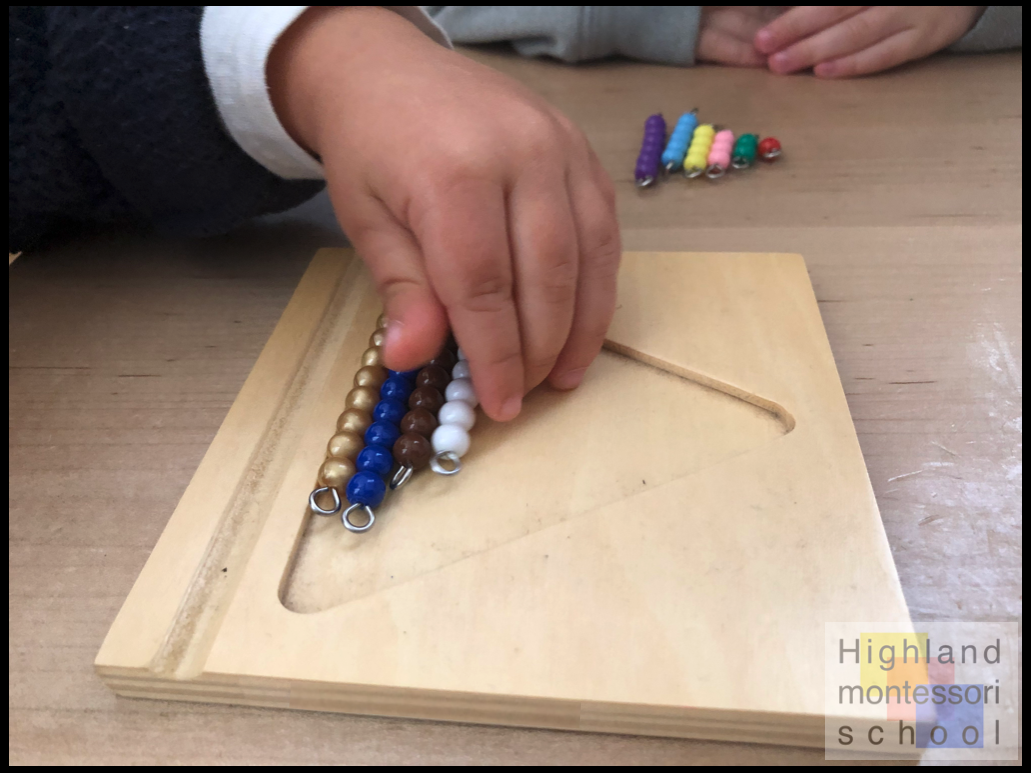
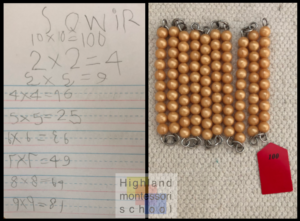 Recently one of our students, just shy of his fifth birthday, pointed to the rack of beaded chains on our wall and asked “What can I do with these?”
Recently one of our students, just shy of his fifth birthday, pointed to the rack of beaded chains on our wall and asked “What can I do with these?”
“You can form them into squares,” the teacher replied, “to help you count them. That’s called multiplication.”
“Is that like when you multiply?” he asked. (Likely a word he picked up from his older sibling, a second grader.)
“Yes, it is. If you get a big workmat, you can start with the twos.” And so began this young child’s journey into multiplication.
In her writings, Maria Montessori often refers to the development of the Mathematical Mind. “Children display a universal love of mathematics,” she said, “which is par excellence the science of precision, order, and intelligence.” We have found this to be true for the youngest children in our classroom.

These little ones–as young as 24 months old–truly crave to keep things in order, seeking out patterns in this world around them and make sense of it all. We see this when the young child stops to watch a line of ants on the playground, lines up her toys on a bench, sorts objects by color or instinctively picks up a spilled tray. One of the first math lessons is “one to one” in which the child is required to place an object (perhaps a small bead or a stone) on a specific spot. A two-step version of this is in the photo at right, where the child first must place a golf tee into the snowman, then place a jingle bell on each tee. This 2-year-old is developing a strong sense of order and repetition that will later be necessary with our counting materials.
The photo at right is a classic Montessori exercise in quantifying, typical of what a 3-year old might do. More than simply counting, this material asks the child to first sort out object (the six gingerbread men or two Christmas trees) and then place them into the appropriately-labeling bins. As Dr Montessori observed over 100 years ago, often the children repeat an activity like this many times before packing it away. They love handling the objects, feeling the weight in their hand as the move them around the table while sorting and counting.
This movement and the visual result of the layout cements the actual sense of quantity in their mind. Having mastered the quantities 1 through 9, the four-year old needing even more objects will move on to our Montessori Bank. This includes our golden

beads–individual units, bars of ten, squares of 100 and cubes of 1,000. The 1,000 cubes are actually 1,000 times heavier than the single bead. Picking up and feeling the weight of the squares, bars and cubes not only takes time, but engages the kinesthetic memory within each child. It is with the bank that the child will learn larger addition and subtraction problems (photo, right).
The idea of quantity which we use at the preschool level is necessary when the child moves on to written math, typically associated with elementary school. But when our students reach that level, they will already know the basic operations–and they will have had fun doing so!
And about the 5-year-old who was building his squares? Check back here in the springtime. We suspect he’ll be doing basic multiplication and division–and then next fall he can move on to Kindergarten!



